The Line-of-Balance (LOB) technique is a project scheduling and management method that is particularly useful for repetitive or continuous production processes. It helps in planning and controlling projects that involve the sequential production of similar units or tasks, such as manufacturing assembly lines, construction projects, or software development.
The LOB technique represents the project's timeline as a single continuous line, hence the name "Line-of-Balance." It focuses on the flow of work rather than individual tasks or activities. The technique divides the project into several repetitive units or work segments, which are referred to as production units.
Here's how the Line-of-Balance technique works:
Identify the repetitive production units: Determine the key units or tasks that will be repeated throughout the project. For example, in construction, it could be the construction of floors in a building or the installation of windows.
Estimate the time required for each production unit: Determine the time required to complete each unit or task. This estimation should consider the resources, manpower, and other factors relevant to the completion of the unit.
Establish the sequence and dependencies: Determine the order in which the production units should be executed. Identify any dependencies between the units. For example, a unit may require completion of another unit before it can begin.
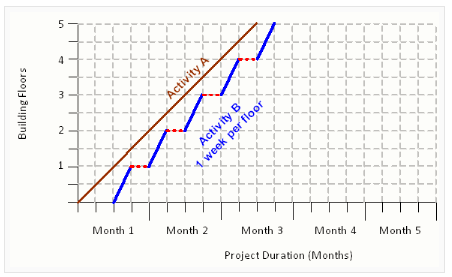
Plot the Line-of-Balance: Create a horizontal line representing the project's timeline. Mark the start and end points on the line. Then, plot the estimated time for each production unit along the line based on their sequence and dependencies.
Allocate resources and manpower: Determine the resources and manpower required for each production unit. This includes assigning specific teams or individuals responsible for each unit. Ensure that resources are effectively allocated to maintain a smooth flow of work along the Line-of-Balance.
Monitor and control progress: As the project progresses, regularly monitor the actual time taken to complete each production unit. Compare it with the planned time to identify any deviations. If there are significant variances, take corrective actions to bring the project back on track.
Continuous improvement: Analyze the project's performance and use the insights gained to improve future iterations of the Line-of-Balance technique. Identify bottlenecks, areas of improvement, and opportunities for optimization.
By using the Line-of-Balance technique, project managers can effectively plan and schedule repetitive tasks, optimize resource allocation, and visualize the overall flow of work. It provides a systematic approach to manage projects with repetitive elements and promotes efficiency and productivity in the project execution.
0 Comments
"Welcome to our blog! We'd love to hear your thoughts on this post. Please leave a comment below."